Architect Carlos Arroyo transforms an old Coca-Cola factory in Belgium into a public center.
The starting point of this project from Carlos Arroyo Arquitectos was a radical remake in situ of the existing industrial building. This included the foundations and sediments, the primary bearings, to isolating and waterproofing the exterior ‘skin’ and the heating and water systems. The project could be described as ‘upcycling’; instead of introducing new materials, what was already there was utilised and given new meaning.
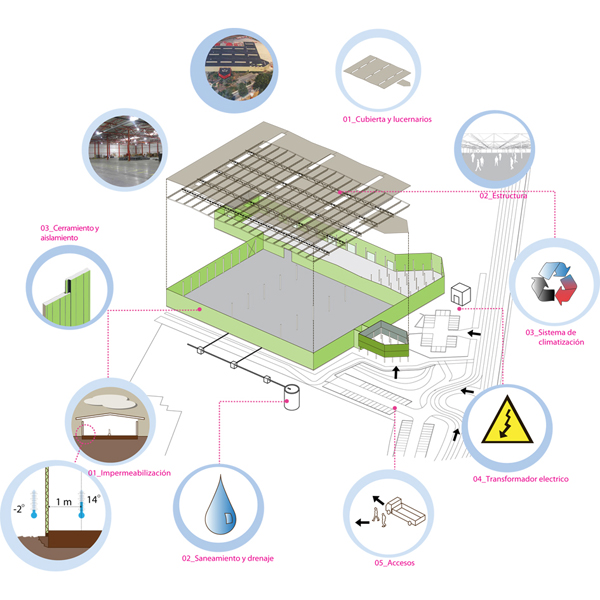 In 2006, the city of Oostkamp acquired the old Coca Cola installations: a 40.000 m2 plot with a 11.000 m2 industrial building dating from 1991. In 2008, the competition brief defined a complex that would gather most of the public services of the city on this central and well-connected plot.
In 2006, the city of Oostkamp acquired the old Coca Cola installations: a 40.000 m2 plot with a 11.000 m2 industrial building dating from 1991. In 2008, the competition brief defined a complex that would gather most of the public services of the city on this central and well-connected plot.
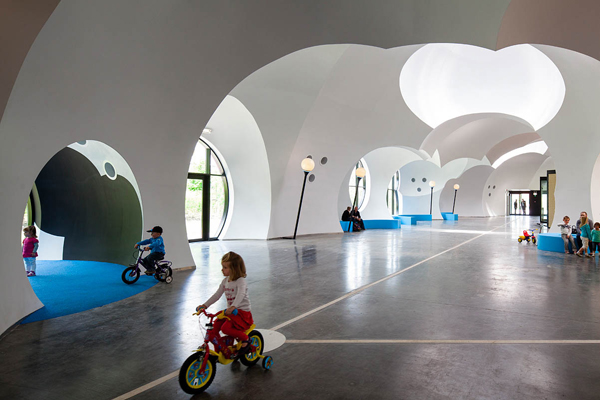
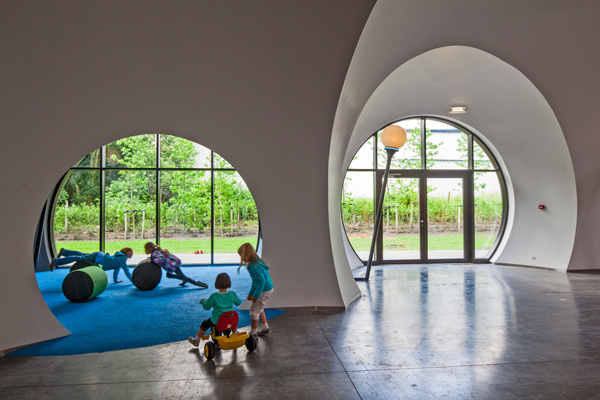
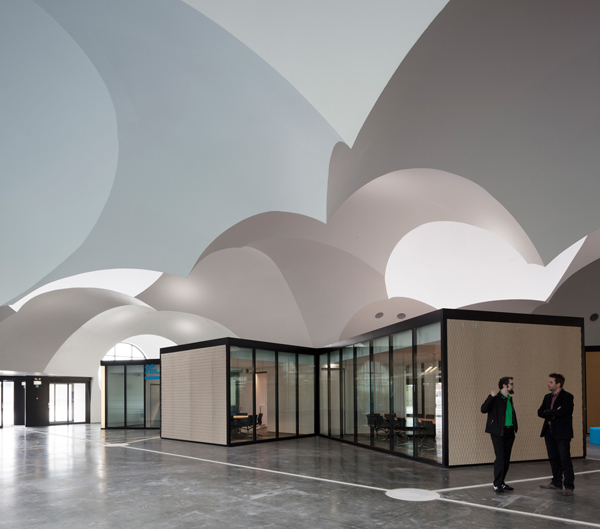
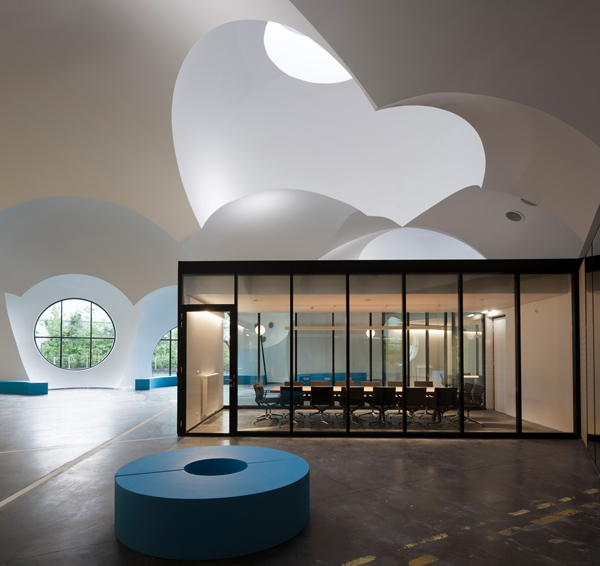
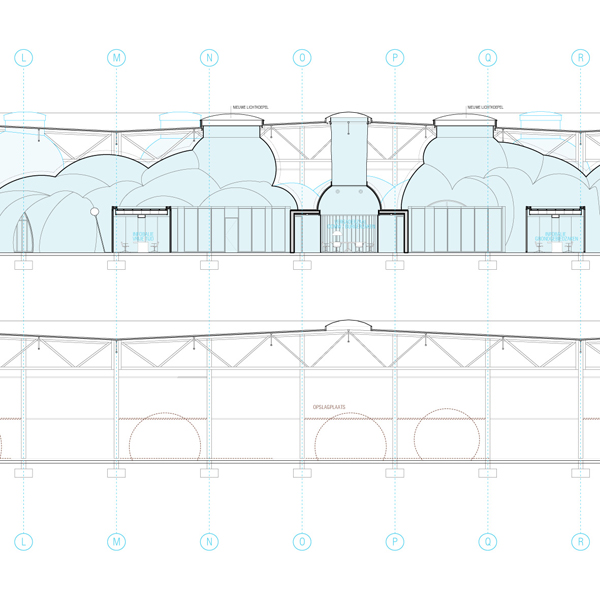
A reutilisation of the large industrial building was decided on, as well as a radical transformation of the interior that converted it into a landscape that recalls luminous ‘white clouds’ inside a sheltered, climate controlled public space. The programme was organised into simple and adaptable modular clusters. Inside, the thin and lightweight ‘white clouds’ are made of plaster reinforced with glass fibre. They are 7-8 millimetros thick and weigh only 7 kg/m2.
 The openings among the clouds are equipped with simple devices that transform all kinds of weather conditions into fun experiences.
The openings among the clouds are equipped with simple devices that transform all kinds of weather conditions into fun experiences.
As well as solving problems of accumulated energy, this solution is also visually exciting. An attitude that fits within the criteria of ‘Sustainable Exuberance’, a new concept of sustainability. Using an interface that reacts to external conditions in an unstable climate, this enormous public building functions on minimal energetic and economic cost.
The interior of the building is like a type of Grand Place. It groups together all the service areas that the City Hall has to offer and creates a new relationship between city administration and citizens.
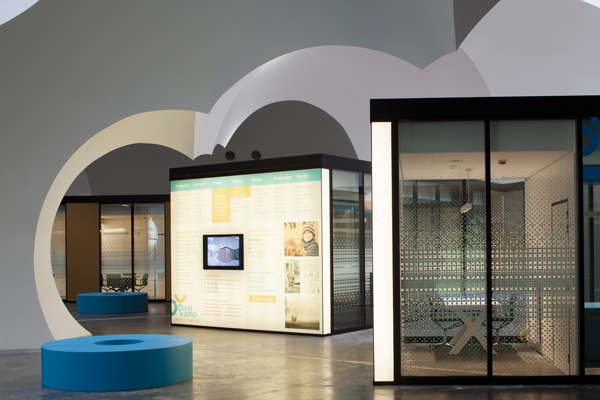
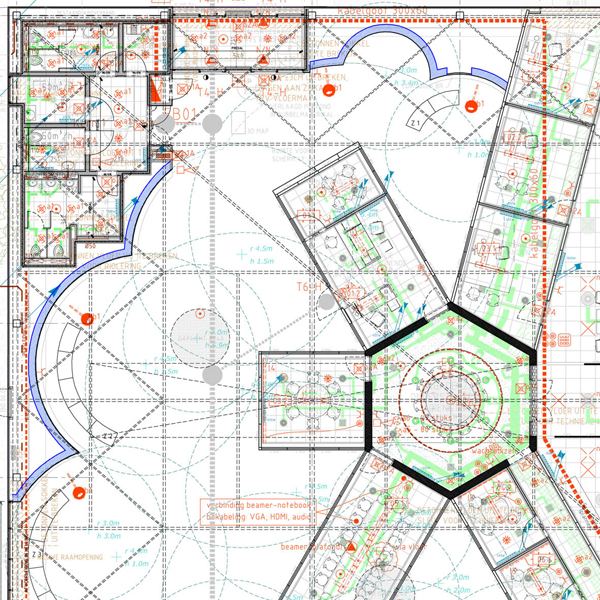
The service areas are represented graphically through a configuration of modules resembling, in the architect’s own words, a central nervous system. The modules, which were conceived through workshops with both citizens and public officials, can be reorganised or amplified effortlessly, saving on cost and manpower.
The information points are situated at the extreme ends of the ‘nerves’. In reality they are a 3D interpretation of the city’s web portal. The digital graphic elements have been reproduced on touch screens so citizens can enter through a ‘frame’ to talk to the person behind the website.
The project has attempted to transmit the values of governmental transparency. The general assembly room is in full view of the public and other meetings occur in common areas, making information easily accessed.
Even the public works department, along with its operations areas and warehouse, are open to all allowing the general public to see the workers in action.
Floor markings direct everybody where to go, not just the visually impaired.
The information points house cantilever tables facilitate ease of movement for visitors in wheel chairs, without appearing as those specially-designed for them.
The programme has aimed to accommodate all sorts of uses, so from weddings to deliveries of construction materials can be happening at the same time. Here you can see a diagram drawn up by the architect that helped them to plan for the predicted movement of people and materials, dust and noise, and how they could be controlled and optimised.
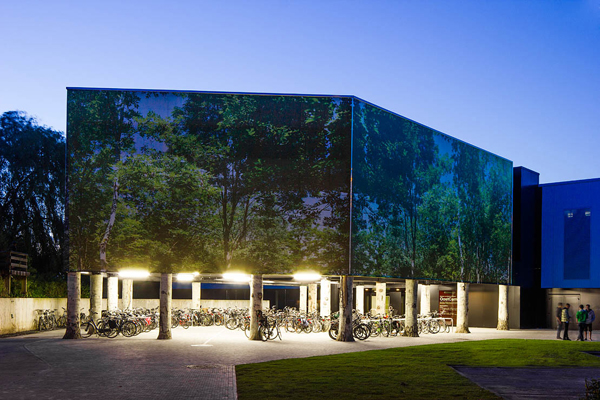
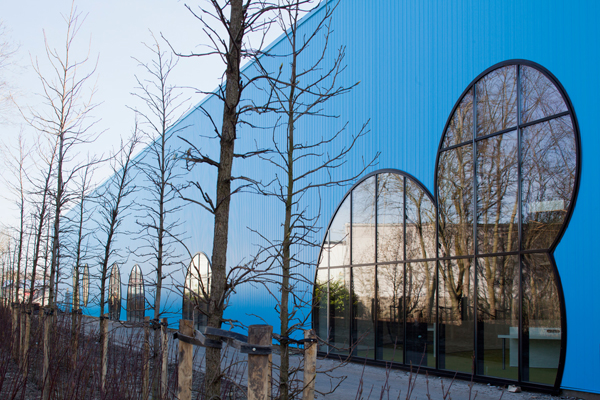
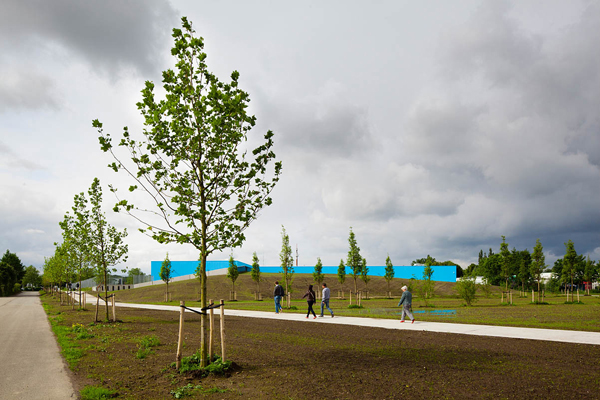
The exterior appears as a non-building. The old red walls of the Coca-Cola plant were covered with a screen representing a forest. This not only boosted the edifice’s solar power producing capacity but also helps to express its commitment to sustainable energy and environmental health.
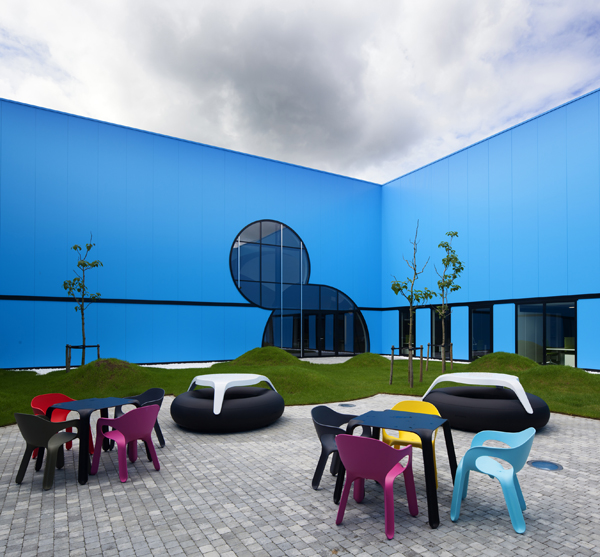
The project is completed with a ‘Productive Park’ made of recycled materials and with bicycle and walking paths.
Photographs: Miguel de Guzmán